On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar System
On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar System
Solar power has gained immense popularity in recent years as a clean and sustainable source of energy. It offers homeowners and businesses an opportunity to reduce their carbon footprint while saving money on energy bills. When considering solar power, two primary options come to mind: off-grid and on-grid solar systems. Each has its unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on various factors. In this, we’ll explore the key differences between on-grid and off-grid solar systems, delve into what they are, and discuss which might be the better choice for your energy needs.
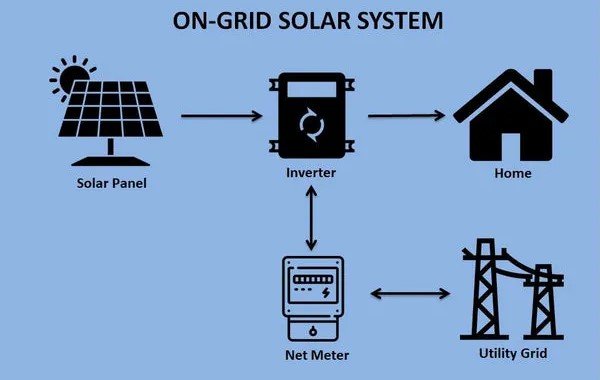
What Is an On-Grid Solar System?
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected system, is designed to work in conjunction with your local utility grid. Here’s how it functions:
- Solar Panels Generate Electricity: Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels installed on your property convert sunlight into electricity.
- Electricity Is Fed into the Grid: The electricity generated by the solar panels is fed into the local utility grid through an inverter, which converts the DC power from the panels into AC power for use in your home and excess is sent to the grid.
- You Consume Electricity from the Grid: Your property draws electricity from the grid when the solar panels aren’t generating enough power (e.g., at night or during cloudy days).
- Net Metering: If your solar panels generate more electricity than you use, the excess is credited to your account. This is known as net metering, which can lead to reduced energy bills or even earn you money.
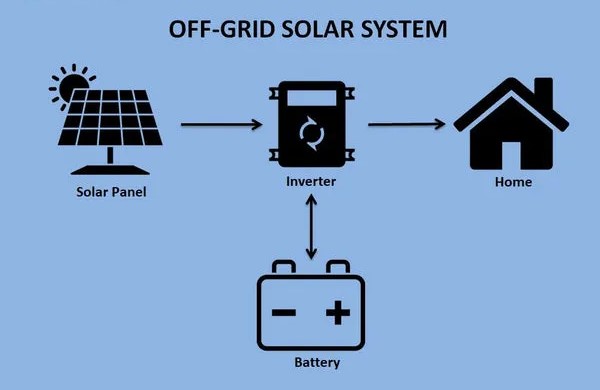
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system, as the name suggests, operates independently of the utility grid. It’s often used in remote areas where access to the grid is limited. Here’s how it works:
- Solar Panels Generate Electricity: Solar panels on your property generate electricity from sunlight, just like with on-grid systems.
- Batteries Store Excess Electricity: Excess electricity generated during the day is stored in batteries for use during the night or when the panels can’t produce power.
- No Connection to the Grid: An off-grid system doesn’t connect to the local utility grid. You rely solely on the solar panels and battery storage for your electricity needs.
